DSL Registry
The DSL Registry is responsible for storing and managing all registered DSL workflows across the platform. It provides a REST API interface to register, update, query, and delete DSL definitions that power decision-making and task orchestration logic.
Functionalities:
- Centralized storage for all DSL workflows
- Metadata-based search, categorization, and filtering
- APIs to register new workflows, update existing ones, or remove obsolete entries
- Integrated with the DSL SDK for remote loading and execution of workflows
DSL DB Registry Architecture
The DSL DB Registry is the central system for managing the lifecycle, validation, indexing, and query operations of modular DSL workflows. It supports the dynamic registration, versioning, and orchestration of DSL-based task pipelines. Architected for extensibility and compliance, the system integrates policy validation, indexing, and event notification pipelines to ensure secure and scalable execution across distributed environments.
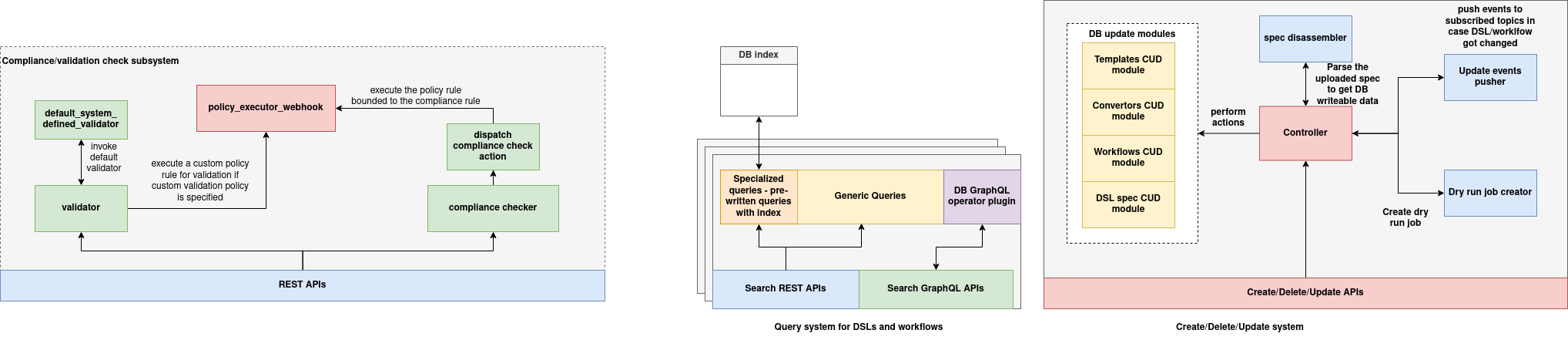
Data Model and Storage Layer
At the heart of the DSL DB Registry lies a versioned, modular, and graph-aware data structure designed to represent complex workflows:
-
workflow_schema: This is the primary entity representing a DSL workflow. It includes fields such asworkflow_id,name,description,version,tags,globalSettings, and agraphstructure that models the execution DAG. Each workflow entry also maintains amodulesmap, where each module has metadata likecodePath,resource_requirements, and execution settings. -
module_schema: Modules are independently defined components of a DSL workflow. Each contains: -
Execution code reference (
codePath) settingsandparametersfor runtime configuration- Metadata fields such as
name,description,tags - Resource definitions for scheduling (e.g., CPU, GPU)
This separation ensures that workflows can evolve modularly, supporting reuse, partial updates, and isolated execution.
Workflow Registration Pipeline
The DSL DB Registry includes a modular pipeline for workflow lifecycle operations, orchestrated through a controller layer:
-
Controller: Receives REST API or file-based (ZIP) submissions. It invokes downstream modules based on the operation type — create, update, delete.
-
Spec Disassembler: Parses uploaded archives (via
/uploadWorkflow) to extract theworkflow.jsondefinition and associatedmodule_directories. Each module is zipped, uploaded to object storage (e.g., S3), and linked via thecodePath. -
DB Update Modules:
-
Templates CUD: Manages reusable workflow templates
- Convertors CUD: Handles transformations between different workflow spec versions
- Workflows CUD: Executes creation, update, and deletion of
workflow_schemaentries -
DSL Spec CUD: Applies global validation and conversion logic for uploaded workflow specs
-
Dry Run Job Creator: Before committing any changes, a simulated dry-run job may be created to validate executability and structural integrity.
-
Update Events Pusher: Broadcasts events to external systems (e.g., UI, search engine, cache invalidators) when a DSL or module is modified.
Compliance and Validation Engine
The DSL registry enforces validation and compliance policies at registration time through a dedicated validation pipeline:
-
validator: Core component that performs both structural and logical checks on incoming workflow definitions. -
default_system_defined_validator: Validates required fields, type safety, DAG structure, and schema conformance. -
policy_executor_webhook: Executes custom validation policies — if specified — using organization-defined rules (e.g., usage limits, dependency constraints). -
compliance_checker: Dispatches policy actions and ensures rule bindings are satisfied before persisting the workflow.
This layered validation approach guarantees that all registered workflows are safe, compliant, and semantically sound.
Search and Indexing Layer
A dual-mode query architecture enables both exact-match and metadata-based DSL discovery:
-
Generic Query Handler: Handles common lookup operations (by tag, name, ID) via optimized REST APIs.
-
Specialized Prewritten Queries: Implements frequently used filters with index-level optimizations.
-
DB Indexes: Built on fields like
tags,workflow_id, andnameto support high-performance search and filtering. -
GraphQL Operator Plugin: Translates complex, user-defined GraphQL queries into optimized MongoDB operations using composable filters.
-
Search APIs:
-
REST APIs: For standard and dynamic queries (
/workflows/query) - GraphQL APIs: For rich, front-end driven explorations with filtering, pagination, and introspection
Event-Driven Consistency
All major update operations (create, update, delete) are propagated across the system via event pushers:
-
Update Events Pusher: Emits messages when a workflow or module changes, allowing systems like UIs, search engines, or monitoring tools to respond in real-time.
-
Dry Run Hook: Optionally simulates workflow registration to test validity, detect missing modules, or verify compatibility with runtime environments.
Integration Points
- DSL Creator Server: A Flask-based microservice for uploading
.zipbundles containingworkflow.jsonand modules - Asset Uploader: Uploads zipped modules to S3 and injects their paths into
codePath - Workflows Client: Communicates with the backend registry to store validated and transformed workflows
DSL registry schema
Here is a structured explanation of the DSL schema fields:
const moduleSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
codePath: { type: String, default: "" },
settings: { type: Object, default: {} },
parameters: { type: Object, default: {} },
name: { type: String, required: true },
description: { type: String, required: true },
tags: { type: [String], default: [] },
resource_requirements: { type: Object, default: {} }
});
const versionSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
releaseTag: { type: String, required: true },
version: { type: String, required: true }
})
const workflowSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
workflow_id: { type: String, required: true, unique: true },
name: { type: String, required: true },
version: { type: versionSchema, required: true },
description: { type: String, required: true },
tags: { type: [String], default: [] },
globalSettings: { type: Object, default: {} },
globalParameters: { type: Object, default: {} },
modules: { type: Map, of: moduleSchema },
graph: { type: Object, default: {} }
}, { _id: false });
Top-Level Fields in workflowSchema
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
workflow_id |
String |
A unique identifier for the DSL workflow. Required. |
name |
String |
Human-readable name for the workflow. Required. |
version |
versionSchema |
An object containing version metadata. Required. |
description |
String |
Description of what the DSL workflow does. Required. |
tags |
[String] |
Optional tags used for search, filtering, and categorization. |
globalSettings |
Object |
Key-value configuration options that apply globally across the workflow. |
globalParameters |
Object |
Parameters applicable at the workflow level (e.g., input configurations). |
modules |
Map<String, moduleSchema> |
Map of modules used in the workflow; keys are module identifiers. |
graph |
Object |
A representation of the workflow DAG (nodes, edges, dependencies). |
versionSchema Fields
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
releaseTag |
String |
A label or tag for the release (e.g., "stable", "beta"). Required. |
version |
String |
SemVer or custom version identifier (e.g., "v1.2.0"). Required. |
moduleSchema Fields (used in modules map)
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
codePath |
String |
Path or URI pointing to the executable code (e.g., Python module, script, etc.). |
settings |
Object |
Module-specific configuration settings (e.g., retry policy, thresholds). |
parameters |
Object |
Input parameters specific to this module. |
name |
String |
Name of the module (for readability and debugging). Required. |
description |
String |
Describes what this module does. Required. |
tags |
[String] |
Tags for categorizing or filtering the module. |
resource_requirements |
Object |
Specifies compute requirements (e.g., CPU, memory, GPU) for scheduling and orchestration. |
DSL registry APIs
The DSL Registry provides a RESTful interface to register, manage, and query DSL workflows used for orchestrating modular task execution across the system.
1. Get All Workflows
Endpoint: GET /workflows
Description: Retrieves all DSL workflows stored in the registry.
Response:
{
"success": true,
"data": [ /* list of workflows */ ]
}
2. Get Workflow by ID
Endpoint: GET /workflows/:workflow_id
Description: Retrieves a specific workflow by its workflow_id.
Path Parameter:
workflow_id(string) – Unique identifier of the workflow.
Response:
{
"success": true,
"data": { /* workflow object */ }
}
404 Response (if not found):
{
"success": false,
"message": "Workflow not found"
}
3. Create a New Workflow
Endpoint: POST /workflows
Description: Creates a new DSL workflow and stores it in the registry. The workflow_id is auto-generated using the format:
<name>:<version.version>-<version.releaseTag>
Request Body:
{
"name": "Example Workflow",
"version": {
"version": "1.0.0",
"releaseTag": "stable"
},
"description": "A test workflow.",
"tags": ["test", "example"],
"globalSettings": { },
"globalParameters": { },
"modules": { },
"graph": { }
}
Response:
{
"success": true,
"data": { /* newly created workflow */ }
}
Error Response:
{
"success": false,
"message": "<error details>"
}
4. Update Workflow by ID
Endpoint: PUT /workflows/:workflow_id
Description: Updates an existing workflow using its workflow_id.
Path Parameter:
workflow_id(string) – The identifier of the workflow to update.
Request Body: (Partial or full workflow object)
Response:
{
"success": true,
"data": { /* updated workflow */ }
}
404 Response (if not found):
{
"success": false,
"message": "Workflow not found"
}
5. Delete Workflow by ID
Endpoint: DELETE /workflows/:workflow_id
Description: Deletes the workflow corresponding to the given workflow_id.
Path Parameter:
workflow_id(string) – Identifier of the workflow to delete.
Response:
{
"success": true,
"data": { /* deleted workflow */ }
}
404 Response (if not found):
{
"success": false,
"message": "Workflow not found"
}
6. Query Workflows (Dynamic Search)
Endpoint: POST /workflows/query
Description: Supports advanced querying of workflows using dynamic MongoDB-style filters.
Request Body:
{
"query": {
"tags": "example"
},
"projection": {
"name": 1,
"workflow_id": 1,
"_id": 0
},
"limit": 10,
"skip": 0,
"sort": {
"name": 1
}
}
query(object) – MongoDB-style filter query.projection(object, optional) – Fields to include/exclude.limit(integer, optional) – Number of results to return (default: 100).skip(integer, optional) – Number of results to skip (for pagination).sort(object, optional) – Sort criteria (e.g.,{ name: 1 }for ascending).
Response:
{
"success": true,
"data": [ /* list of matching workflows */ ]
}
DSL Creator Server
The DSL Creator Server is a lightweight Flask-based API that allows users to upload a packaged DSL workflow archive (ZIP file). The server processes the archive, extracts and zips each module, uploads them to a configured S3 bucket, and registers the complete DSL definition with a persistent backend workflow registry.
This enables users to create complex DSL workflows and register them in a single upload action.
What the Server Does
When a user uploads a .zip file to the /uploadWorkflow endpoint:
- The archive is temporarily saved and extracted.
- The server looks for a
workflow.jsonfile at the root. -
All subdirectories prefixed with
module_are: -
Individually zipped
- Uploaded to a configured S3 bucket via
AssetUploader - Mapped back into the
codePathof the module inside theworkflow.json - The
workflow.json(now updated withcodePathURLs) is sent to the backend workflow registry API via theWorkflowsClient.
This fully automates the packaging, deployment, and registration of modular workflows.
API Reference
POST /uploadWorkflow
Uploads a complete DSL workflow ZIP archive and registers it with the backend registry.
Request
- Content-Type:
multipart/form-data -
Form field:
file— the ZIP file containing: -
workflow.json - One or more module folders prefixed with
module_
Example curl Request
curl -X POST http://<host>:5000/uploadWorkflow \
-F "file=@/path/to/my_workflow.zip"
ZIP Structure Requirements
my_workflow.zip
├── workflow.json
├── module_module1/
│ ├── function.py
│ └── requirements.txt (optional)
├── module_module2/
└── ...
Response
- Success (200):
{
"success": true,
"workflow_id": "example_workflow",
"message": "Workflow created successfully"
}
- Client Error (400): Missing file or bad workflow content
{
"success": false,
"message": "No file provided"
}
- Server Error (500): Internal error during processing or upload
{
"success": false,
"message": "Error processing workflow zip: <error message>"
}